80 Year Old Has Vertigo Dizzines Blue Lips
POTS (Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome) is often called "the invisible disease". This reference is no accident. POTS is dificult to detect and diagnose. As a cardiologist with experience diagnosing and treating POTS Syndrome, I hope this article will remove the proverbial "invisible veil" by explaining signs and symptoms of POTS.
 Orthostasis and Tachycardia (Dizziness When Standing & Fast Heart Rate)
Orthostasis and Tachycardia (Dizziness When Standing & Fast Heart Rate)
These are the hallmark symptoms of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome. Orthostasis is basically a sensation of dizziness upon standing, and tachycardia is a fast heart rate. The definition often used for POTS is symptoms on standing, accompanied by an increase in heart rate of 30 beats per minute within 10 minutes of standing. Although there may be a sensation of fainting, most POTS patients don't pass out.
Why POTS Patients Experience Dizziness & Fast Heart Rate
Usually on standing there is an immediate shift of about ½ a liter of blood from the upper body to the lower body. There is also shift of blood out of the blood vessels in to the surrounding tissues. The problem with this is that enough blood still needs to go back to the heart and the upper body to function normally. In a normal scenario, the body responds by tightening the blood vessels and returning more blood to the heart and a slight increase in heart rate. In POTS, this response is abnormal resulting in a pooling of blood in the lower body. The heart rate increases excessively to try and counteract this, but it's often not enough and creates the orthostatic symptoms (fast heart rate), often the source of other symptoms of POTS Syndrome.
POTS Syndrome Symptoms Cheat Sheet
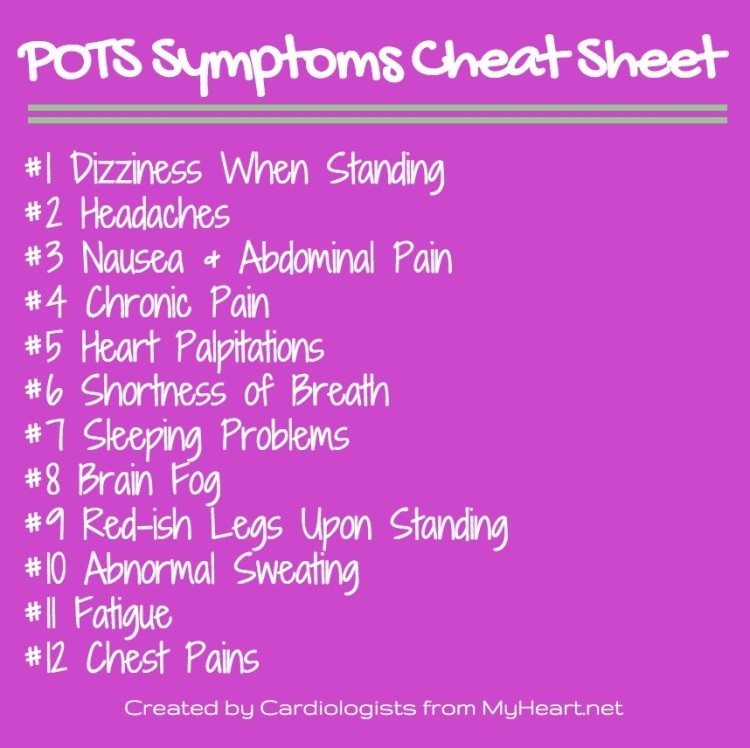
Headaches
About two-thirds of POTS patients experience headaches as symptoms of POTS syndrome (Mack et al). Migraine headaches, the most intense kind, are common and bring with them additional symptoms such as nausea, a sense that the room is spinning, dizziness, and finding loud noises and bright light extremely bothersome. Coat hanger headaches, which primarily cause pain in the head and shoulders, are a highly common and troubling symptom among those diagnosed with POTS (Khurana et al). Coat hanger headaches are often worsened with standing or exercise and relieved by rest.
Stomach (Nasuea & Abdomnimal Pain) Symptoms
In addition to the symptoms of dizziness and difficulty maintaining a standing position, many POTS symptoms experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and abdominal pain. In some patients, it has been found that treatment of the POTS, leads to improvement in the stomach symptoms (Sullivan et al). A lot of POTS symptoms are attributed to a dysfunctional nervous system that prevents blood return to the upper body when standing. It has also been shown that some of the gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with orthostatic intolerance can similarly be attributed to a dysfunctional nerve supply to the stomach (Seligman et al). Other reported complaints include bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is defined as persistent pain, lasting more than 3-6 months, and may include symptoms such as the headaches and the gastrointestinal symptoms described above. Unfortunately and frustratingly, despite extensive evaluations, many chronic pain patients find no clear underlying cause. This makes it difficult to treat this symptoms. Like many other POTS syndrome symptoms, chronic pain may partly be explained by disruption of the nervous system, but is overall poorly understood (Eccleston et al).
Visualization of Four Primary POTS Symptoms
Heart Symptoms – Chest Pains, Palpitations and Shortness of Breath
Heart related symptoms are fairly common amongst POTS patients. Palpitations are often reported and although these are typically relatively harmless often a monitor will be used to evaluate them better and to rule out easily treatable problems. Chest pains are also commonly reported, although these are once again usually benign in nature. Shortness of breath and fatigue may also be reported, particularly on activity, however the pumping function of the heart is usually normal in POTS patients, although it has been reported that the heart is relatively small compared to healthy subjects.
Symptoms Related to Menstrual Cycle in Women
The majority of POTS patients are younger women. 80% of these report a worsening of their symptoms during the menstrual cycle. In addition there is a higher likelihood of gynecologic abnormalities such as ovarian cysts, dysfunctional bleeding and endometriosis (Peggs et al).
Problems Sleeping
Sleep disturbances have been well described in POTS syndrome. Symptoms include poor sleeping at night, waking up repeatedly at night, and sweating at night. POTS patients were found to have more sleep disturbances and higher levels (Bagai et al).
Brain Fog
A common POTS symptom is impairment of cognitive function. Cognitive function basically means intellectual processing. Amongst POTS syndrome patients this is often called 'brain fog'. Almost all POTS patients experience some degree of brain fogging. Patients most commonly describe brain fog as as difficulty focusing, thinking, and communicating (Ross et al).
Dark-Red / Bluish Legs on Standing
About 50% of POTS patients have something called dependent acrocyanosis. This basically means dark red or bluish color to the legs typically on standing. The exact cause is not known. It's usually painless and the legs continue to function as normal.
Sweating Abnormalities
Both increased and decreased sweating have been described in POTS patients. In the hyperadrenergic form of POTS there may be profuse sweating episodes.
Other Reported Symptoms
A research paper out of the Mayo Clinic in 2007 reported symptoms of 152 POTS patients that had been evaluated there (Thieben et al). Some of these are listed below, along with the percentages of patients that reported these symptoms. It must be remembered that this is only one study, although it does help our insight in to the symptoms associated with POTS.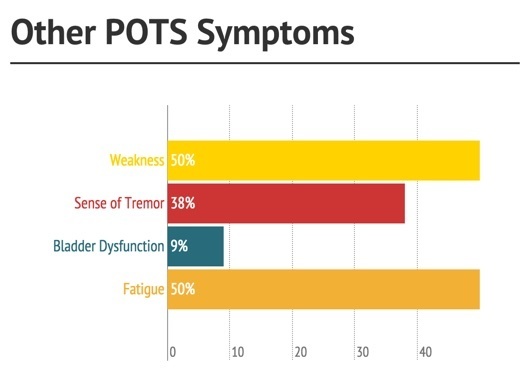
In addition to these symptoms, there is a large list of non-specific symptoms that have been reported by POTS patients. It is difficult to know whether these are related to the POTS syndrome or other problems that exist at the same time. Ongoing research will hopefully help us to better characterize POTS Syndrome and treat its symptoms.
Source: https://myheart.net/pots-syndrome/pots-symptoms-signs/